Recent decades have been marked by the emergence of diseases that move from animals to humans. These are known as zoonotic diseases and examples include Ebola, SARS, MERS, West Nile and Rift Valley fevers. Since there is low resistance to these novel diseases, they have had high impacts on infected human populations, and, in the recent emergence of COVID-19, have reached pandemic status. The United Nations ascribes the emergence of these diseases to the destruction of nature, causing the animal carriers of the disease to come into closer and more frequent contact with people as a consequence of loss of their natural habitat. Exploitation of wildlife and destruction of environments, both global change drivers, are driving the emergence of these diseases among people.
Read More
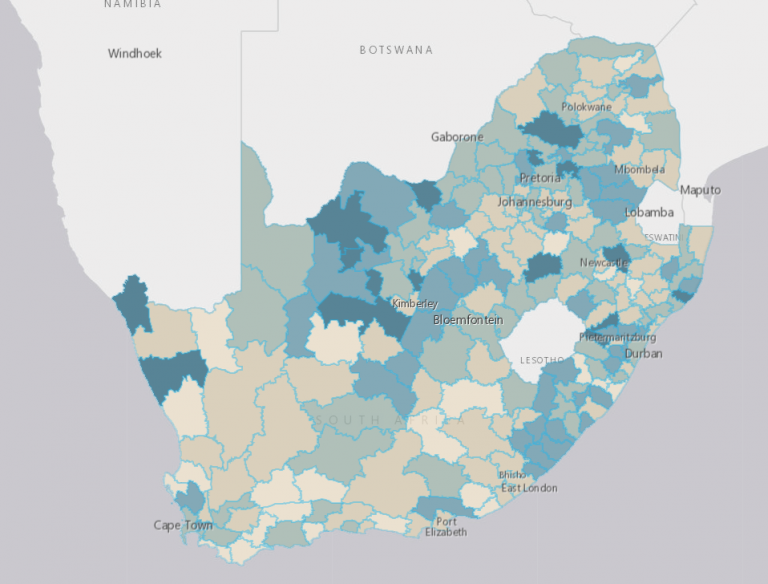













 Health and well-being indicators have been identified from publicly available Health Systems Trust (HST), which has more than 250 indicators of delivery of selected healthcare services in the public health sector across the provinces, districts and local municipalities/sub-districts of South Africa. A reformatted version of the 2018/2019 District Health Barometer (DHB) health indicator dataset provided by the HST is available for download.
Health and well-being indicators have been identified from publicly available Health Systems Trust (HST), which has more than 250 indicators of delivery of selected healthcare services in the public health sector across the provinces, districts and local municipalities/sub-districts of South Africa. A reformatted version of the 2018/2019 District Health Barometer (DHB) health indicator dataset provided by the HST is available for download. This dataset demarcates the boundaries of the health subdistricts across South Africa. Health subdistricts were generated in the largest metropolitan municipalities in South Africa including the City of Cape Town, City of Ekurhuleni, City of Johannesburg, City of Tshwane, Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality, Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality.
This dataset demarcates the boundaries of the health subdistricts across South Africa. Health subdistricts were generated in the largest metropolitan municipalities in South Africa including the City of Cape Town, City of Ekurhuleni, City of Johannesburg, City of Tshwane, Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality, Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality. 